Creating a water-smart vertical gardening schedule is essential for growing thriving plants while conserving precious resources. By understanding how climate, plant types, and evaporation rates affect water needs, you can develop a customized watering routine that maximizes efficiency in limited spaces. This comprehensive guide will walk you through creating a precise watering schedule that saves water, reduces maintenance time, and produces healthier plants in your vertical garden.
Understanding Evaporation Rates
Evaporation rates directly impact how quickly your vertical garden loses moisture
What Are Evaporation Rates & Why Do They Matter?
Evaporation rate refers to how quickly moisture leaves the soil and plants in your garden. This natural process is influenced by temperature, humidity, wind, and sunlight exposure. Understanding evaporation is crucial because it determines how frequently you need to water your vertical garden.
In vertical gardens, evaporation happens more quickly than in traditional gardens for several reasons. The limited soil volume in containers holds less moisture, vertical structures often receive more direct sunlight and wind exposure, and gravity pulls water downward, potentially leaving upper plants drier than lower ones.
By measuring and accounting for evaporation rates in your specific location, you can create a watering schedule that delivers precisely what your plants need—no more, no less.
How to Measure Evaporation in Your Garden
Creating your own evaporation measurement system is surprisingly simple. Here’s how to track water loss in your vertical garden:
In arid climates, you might see 0.25-0.3 inches of water loss daily during summer, while humid regions might lose only 0.1 inches. These measurements provide a baseline for your watering schedule, which you’ll then adjust based on plant types and container sizes.
Pro Tip: Place multiple measurement containers at different heights in your vertical garden. Evaporation rates often vary significantly between the top and bottom of vertical structures due to differences in sun exposure and air circulation.
Climate-Specific Watering Strategies

Adjusting for Arid vs. Humid Regions
Your local climate dramatically affects how you should approach watering your vertical garden. What works in Phoenix won’t work in Miami, and understanding these differences is key to water-smart gardening.
Arid Climate Strategies
Humid Climate Strategies
In arid regions, water conservation is paramount. Your vertical garden will likely need more frequent watering but with methods designed to minimize evaporation. In humid areas, the challenge shifts to preventing moisture-related diseases while still ensuring plants receive adequate water.
Seasonal Adjustments
A water-smart vertical gardening schedule must evolve with the seasons. Plants’ water needs change dramatically throughout the year, and your irrigation approach should adjust accordingly.
| Season | Watering Frequency | Watering Volume | Special Considerations |
| Spring | Every 2-3 days | Moderate | Monitor new growth needs; adjust as temperatures rise |
| Summer | Daily to twice daily | High | Water early morning; consider afternoon shade |
| Fall | Every 3-4 days | Moderate to low | Reduce gradually as temperatures drop |
| Winter | Every 7-10 days | Low | Water midday when temperatures are highest |
Remember that these are general guidelines. Your specific climate might require adjustments, especially during unusual weather patterns. Always monitor your plants’ condition and soil moisture rather than rigidly following a calendar.
Plant-Specific Water Needs

Drought-Tolerant vs. Thirsty Plants
One of the most important aspects of creating a water-smart vertical gardening schedule is understanding the vastly different water requirements of various plants. Grouping plants with similar needs together—a practice called hydrozoning—allows you to water efficiently without wasting resources.
Low Water Needs
(Water when top 2″ of soil is dry)
Medium Water Needs
(Water when top 1″ of soil is dry)
High Water Needs
(Keep soil consistently moist)
When designing your vertical garden, try to group plants with similar water requirements on the same irrigation line or in the same section. This practice prevents both overwatering drought-tolerant plants and underwatering thirsty varieties.
Root Depth & Container Size
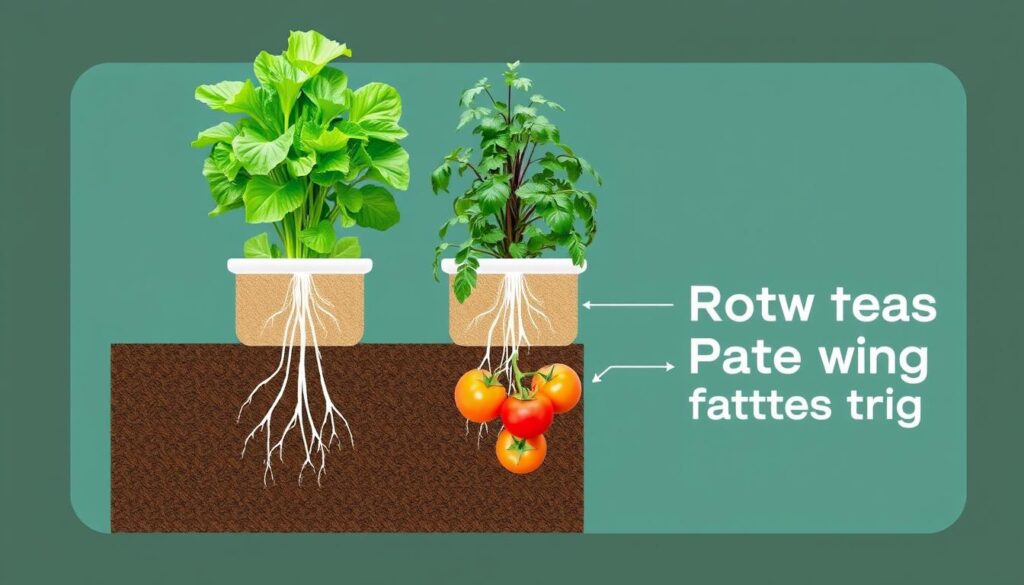
Root depth plays a crucial role in determining watering frequency and volume. Plants with shallow root systems need more frequent but lighter watering, while deep-rooted plants prefer less frequent but deeper soaking.
| Root Depth | Example Plants | Container Depth | Watering Strategy |
| Shallow (2-4″) | Lettuce, Herbs, Strawberries | 6-8 inches | Frequent, light watering; keep top layer consistently moist |
| Medium (6-12″) | Bush Beans, Peppers, Kale | 10-14 inches | Moderate frequency; allow top inch to dry between waterings |
| Deep (12″+) | Tomatoes, Cucumbers, Squash | 16+ inches | Less frequent, deep watering; allow top 2 inches to dry |
Container size directly impacts how quickly soil dries out. Smaller containers hold less moisture and require more frequent watering. When planning your vertical garden, match container depth to the root needs of your chosen plants, and consider using self-watering containers for plants with high water requirements.
“The key to water-smart gardening isn’t just about how often you water, but understanding the relationship between plant type, root depth, container size, and environmental conditions.”
Building Your Custom Watering Schedule

Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a water-smart vertical gardening schedule requires combining your knowledge of evaporation rates, plant needs, and container characteristics. Follow these steps to develop a customized plan that’s efficient and effective:
- Low-water plants: 0.3-0.5 × evaporation rate
- Medium-water plants: 0.7-1.0 × evaporation rate
- High-water plants: 1.2-1.5 × evaporation rate
- Small containers (under 1 gallon): Increase frequency by 30-50%
- Medium containers (1-3 gallons): Use calculated frequency
- Large containers (over 3 gallons): Decrease frequency by 20-30%
- Hot, dry climate: Increase frequency by 20-30%
- Moderate climate: Use calculated frequency
- Cool, humid climate: Decrease frequency by 20-30%
Let’s look at a practical example for a small balcony vertical garden in a dry climate:
| Garden Zone | Plants | Daily Evaporation | Adjustment Factor | Watering Schedule (Summer) |
| Top (most sun/wind) | Herbs (rosemary, thyme) | 0.25 inches | 0.5 × evaporation | 0.125 inches every 2 days |
| Middle | Leafy greens, strawberries | 0.2 inches | 1.0 × evaporation | 0.2 inches daily |
| Bottom (least sun/wind) | Lettuce, spinach | 0.15 inches | 1.2 × evaporation | 0.18 inches daily |
Remember: This schedule is a starting point. Observe your plants closely and adjust as needed. Signs of overwatering include yellowing leaves and soggy soil, while underwatering shows up as wilting and dry, cracked soil.
Tools to Automate & Monitor
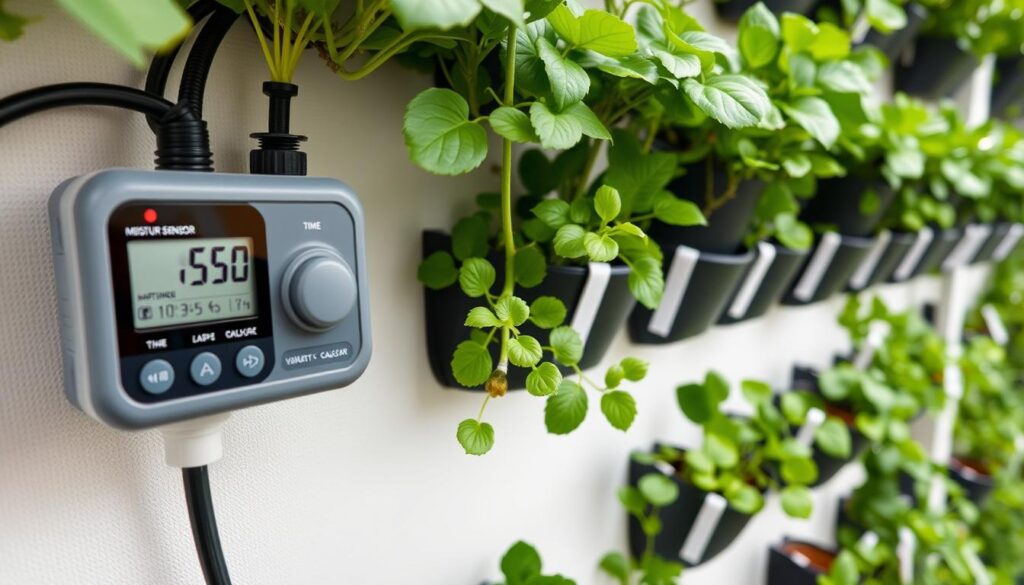

The right tools can make maintaining your water-smart vertical gardening schedule much easier. Here are some essential components to consider:
Irrigation Systems
Timers & Controllers
Monitoring Tools
For most home vertical gardens, a simple drip irrigation system with a programmable timer provides an excellent balance of efficiency and affordability. Adding moisture sensors can further refine your watering by preventing irrigation when the soil is already adequately moist.
Case Studies & Troubleshooting
Example 1: Urban Rooftop Garden in Phoenix, AZ
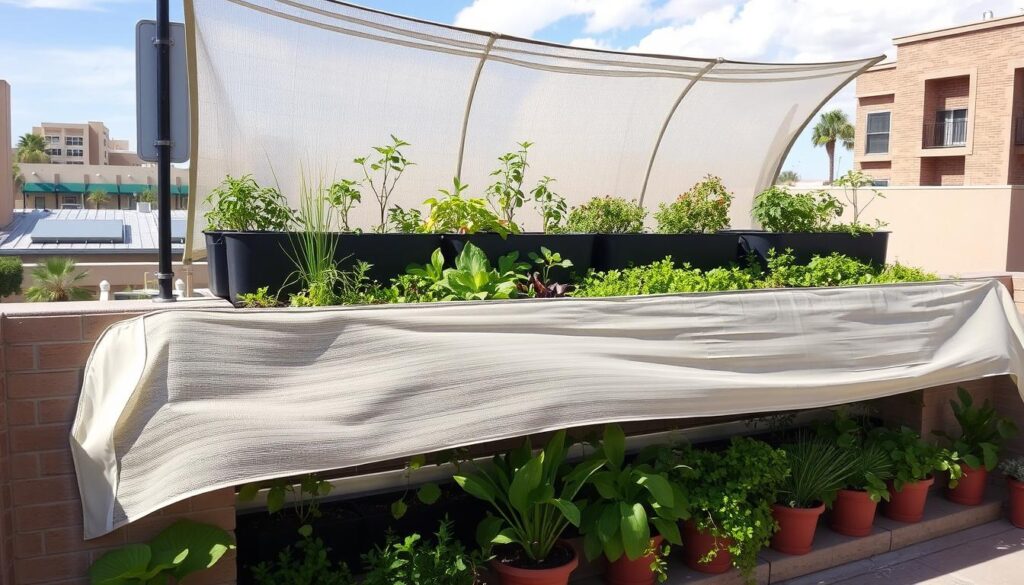

Challenge:
Sarah’s rooftop vertical garden faced extreme conditions: summer temperatures regularly exceeding 105°F, intense direct sunlight, and strong winds that accelerated evaporation.
Solution:
Results:
Despite challenging conditions, Sarah’s vertical garden thrived while using 40% less water than her previous traditional container garden. The morning and evening watering schedule prevented water loss from evaporation, while the shade cloth reduced stress on plants during peak heat hours.
Example 2: Apartment Balcony Garden in Seattle, WA
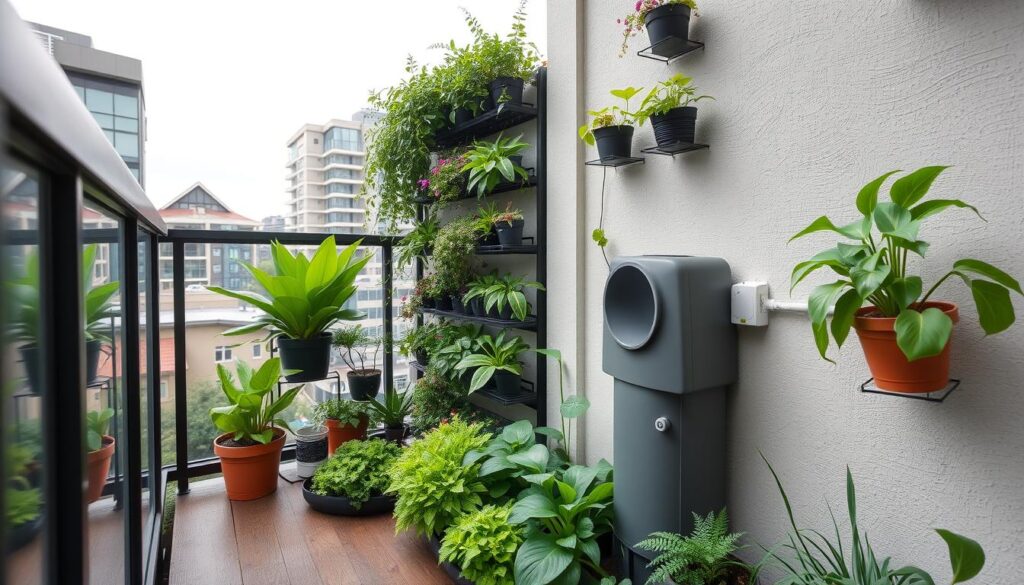

Challenge:
Michael’s north-facing apartment balcony received limited direct sunlight and high rainfall, but also experienced dry periods in summer. His main issues were preventing root rot during rainy seasons while ensuring adequate moisture during dry spells.
Solution:
Results:
Michael’s system automatically adjusted to weather conditions, preventing overwatering during Seattle’s rainy periods while providing consistent moisture during dry spells. His rainwater collection system met nearly 80% of his garden’s water needs throughout the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Best Practices
- Test soil moisture before watering
- Water deeply but less frequently
- Group plants with similar water needs
- Adjust watering schedule seasonally
- Use mulch to retain moisture
- Water early morning or evening
Common Mistakes
- Following a rigid schedule regardless of conditions
- Watering during midday heat
- Overwatering succulents and drought-tolerant plants
- Ignoring signs of over/under watering
- Using containers without proper drainage
- Neglecting to adjust for seasonal changes
Warning: One of the biggest mistakes in vertical gardening is assuming all plants in the structure need the same amount of water. Plants at the top typically need more frequent watering than those at the bottom due to gravity, wind exposure, and heat rising.
Conclusion: Your Path to Water-Smart Success

Creating an effective water-smart vertical gardening schedule isn’t about following a one-size-fits-all approach. It’s about understanding the unique factors that influence your garden’s water needs and developing a customized system that responds to those specific conditions.
By measuring evaporation rates, grouping plants strategically, implementing efficient irrigation, and regularly monitoring and adjusting your approach, you can create a vertical garden that thrives while conserving water. Remember that your schedule should evolve as seasons change, plants mature, and you gain experience with your particular setup.
Start with the framework outlined in this guide, but don’t be afraid to experiment and adapt based on your observations. The most successful water-smart gardeners are those who pay attention to their plants’ signals and respond accordingly.
Ready to Optimize Your Vertical Garden?
Download our free Water-Smart Vertical Garden Schedule Template to create your customized watering plan. This printable resource includes tracking sheets, seasonal adjustment guides, and plant-specific watering recommendations.
With thoughtful planning and consistent application of water-smart principles, your vertical garden can become a thriving, sustainable oasis that produces beautiful results while conserving one of our most precious resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I’m overwatering my vertical garden?
Signs of overwatering include yellowing leaves, soggy soil that doesn’t dry out between waterings, fungal growth on soil surface, and a general wilted appearance despite wet soil. If you notice these symptoms, reduce watering frequency and ensure your containers have proper drainage.
Can I use the same watering schedule year-round?
No, your water-smart vertical gardening schedule should change with the seasons. Plants typically need more water during hot, dry periods and less during cool, humid seasons. Adjust your watering frequency and volume based on seasonal changes in temperature, humidity, and plant growth stages.
What’s the best time of day to water a vertical garden?
Early morning (5-9 AM) is generally the best time to water vertical gardens. This gives plants access to moisture during the day’s heat while allowing foliage to dry before evening, reducing disease risk. In extremely hot climates, a second light watering in early evening may be beneficial.
How do I adjust my watering schedule when it rains?
After rainfall, check the moisture level in your vertical garden’s soil before resuming your regular watering schedule. Remember that vertical gardens, especially those with overhangs or against walls, may receive less natural rainfall than horizontal gardens. A rain gauge can help you measure exactly how much water your garden received.
Will is a vertical gardening enthusiast and sustainable cultivation specialist with a passion for helping people grow fresh food in small spaces and dry climates. With years of hands-on experience testing smart irrigation systems, optimizing urban gardens, and exploring eco-friendly solutions, this author shares clear, practical tips to turn any corner into a productive garden. Whether on a sunny balcony or in a compact backyard, Will helps readers save water, maximize space, and enjoy healthy harvests year-round. When not tending to his plants, you’ll find him sipping herbal tea and sketching ideas for new sustainable projects.

