Vertical gardening in high-heat zones presents unique challenges that can make or break your plants’ survival. When temperatures soar, even the most drought-tolerant plants struggle without proper protection. A well-designed shade cover can be the difference between a thriving vertical garden and crispy, withered plants. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through creating an effective, customizable shade solution specifically designed for vertical gardens in hot climates—helping you extend your growing season, conserve water, and protect your precious plants from extreme heat stress.
Why Vertical Gardens Need Shade in High-Heat Zones
Vertical gardens are particularly vulnerable to heat stress due to their exposed position and limited soil volume. In high-heat zones, temperatures above 90°F (32°C) can quickly damage plants, especially when combined with intense direct sunlight. Without protection, your carefully cultivated vertical garden can suffer from rapid moisture loss, leaf scorch, and stunted growth.
Heat stress can quickly damage vertical garden plants, causing wilting and leaf scorch
The Science Behind Heat Stress in Vertical Plants
Vertical gardens face unique heat challenges compared to traditional gardens. The limited soil volume heats up faster, and the vertical orientation often means plants receive more direct sunlight throughout the day. When temperatures exceed 90°F (32°C), plants struggle to maintain proper water balance through transpiration. The combination of hot air and intense sunlight can raise leaf temperatures to damaging levels, causing cellular damage and disrupting photosynthesis.
Common Signs of Heat Stress:
- Wilting despite adequate watering
- Leaf curling or rolling
- Brown leaf edges (leaf scorch)
- Stunted growth and reduced flowering
- Premature fruit drop
Benefits of Proper Shading:
- Reduces leaf temperature by 10-15°F
- Decreases water evaporation by up to 50%
- Extends growing season by 4-8 weeks
- Prevents sunscald on fruits and vegetables
- Improves overall plant vigor and yield
Benefits of Shade Covers: Water Savings and Yield Protection
Installing a shade cover for your vertical garden isn’t just about preventing heat damage—it’s a smart water conservation strategy. Studies show that properly shaded plants can reduce water needs by 30-50% during peak summer months. For vertical gardens, which already require careful water management, this saving is significant.
In my Arizona vertical garden, adding a 50% shade cloth extended my growing season by nearly two months and cut my summer water usage by almost 40%. The difference in plant health was remarkable within just one week of installation.
Beyond water savings, shade covers protect your harvest. Many vegetables and herbs grown in vertical gardens—like lettuce, spinach, and basil—are particularly sensitive to heat and direct sun. A proper shade solution can mean the difference between abundant harvests and disappointing yields.
Planning Your Vertical Garden Shade Cover Project
Assessing Sun Exposure and Heat Patterns
Before building your shade cover, take time to observe how sunlight interacts with your vertical garden throughout the day. This crucial step ensures your shade solution addresses your specific needs.
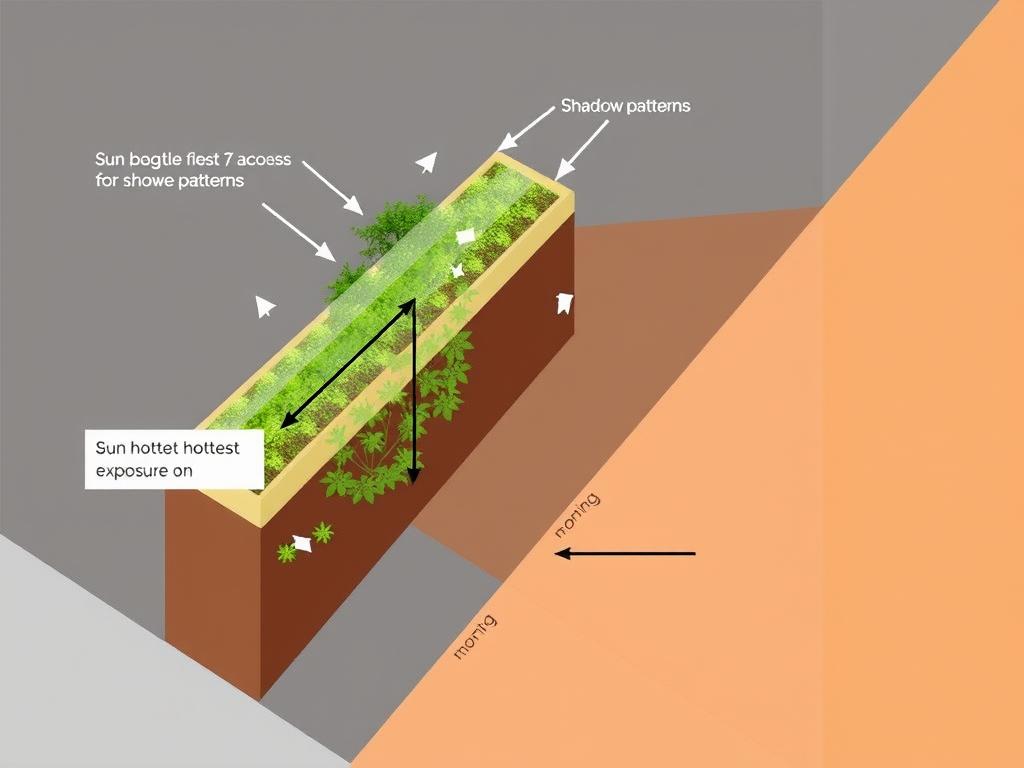
Understanding sun patterns helps determine optimal shade cover placement and design
Pro Tip: In the Northern Hemisphere, west and southwest exposures typically need the most protection. East-facing vertical gardens benefit from morning sun but should be shaded by early afternoon.
Choosing Materials: UV-Resistant Fabrics vs. Natural Options
The material you select for your vertical garden shade cover significantly impacts its effectiveness and longevity. Here’s a comparison of the most popular options:
| Material | Shade % | Durability | Cost | Best For |
| White Knitted Shade Cloth | 30-50% | 3-5 years | $-$$ | Most vegetables and herbs |
| Aluminet Reflective Cloth | 40-60% | 5-7 years | $$$ | Extreme heat zones |
| Bamboo Screens | 50-70% | 2-3 years | $$ | Aesthetic gardens, partial shade plants |
| Shade Sails | 70-90% | 7-10 years | $$$-$$$$ | Permanent installations, large areas |
| Burlap/Jute Cloth | 30-40% | 1 season | $ | Temporary solutions, eco-friendly approach |
For most vertical gardens in high-heat zones, a white knitted shade cloth with 30-50% density offers the best balance of protection, durability, and cost. The white color reflects heat while allowing diffused light to reach your plants.
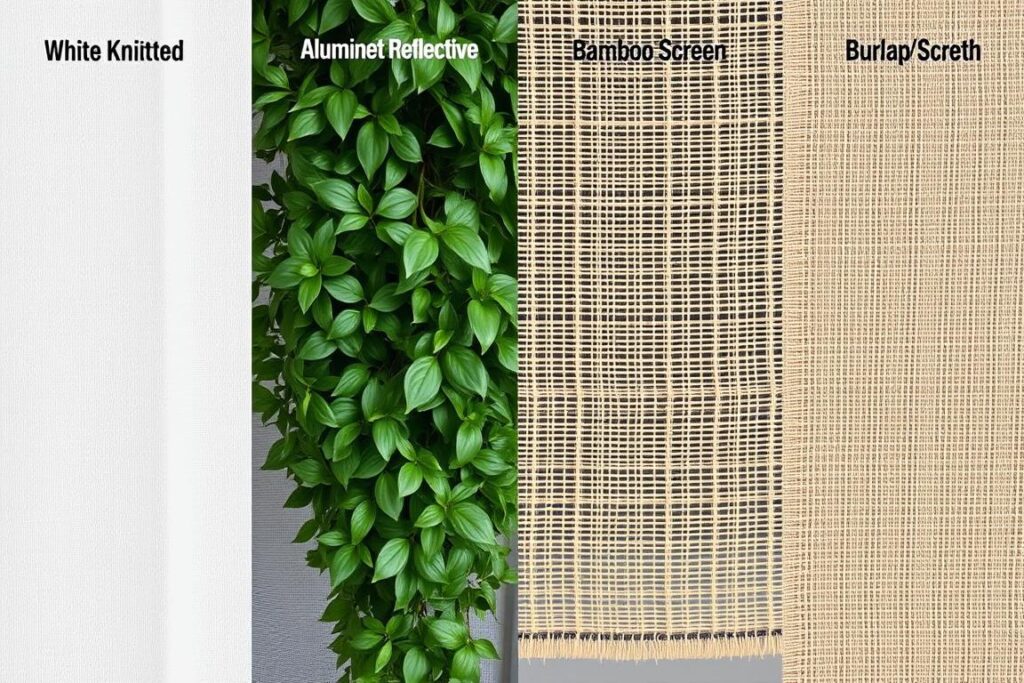

Common shade materials: (L-R) White knitted shade cloth, aluminet, bamboo screen, and burlap
Free Resource: Shade Material Comparison Chart
Download our detailed comparison chart to help select the perfect shade material for your vertical garden’s specific needs and climate conditions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a DIY Vertical Garden Shade Cover
Tools and Materials Checklist
Tools Needed:
- Measuring tape
- Scissors or utility knife
- Drill with bits
- Screwdriver
- Level
- Ladder (if needed)
- Pliers
Materials Needed:
- Shade cloth (sized for your garden plus 10% extra)
- Grommets kit or zip ties
- Eye hooks or brackets
- Tension wire or bungee cords
- PVC pipes or aluminum poles (for frame)
- Carabiners or S-hooks
- UV-resistant cable ties
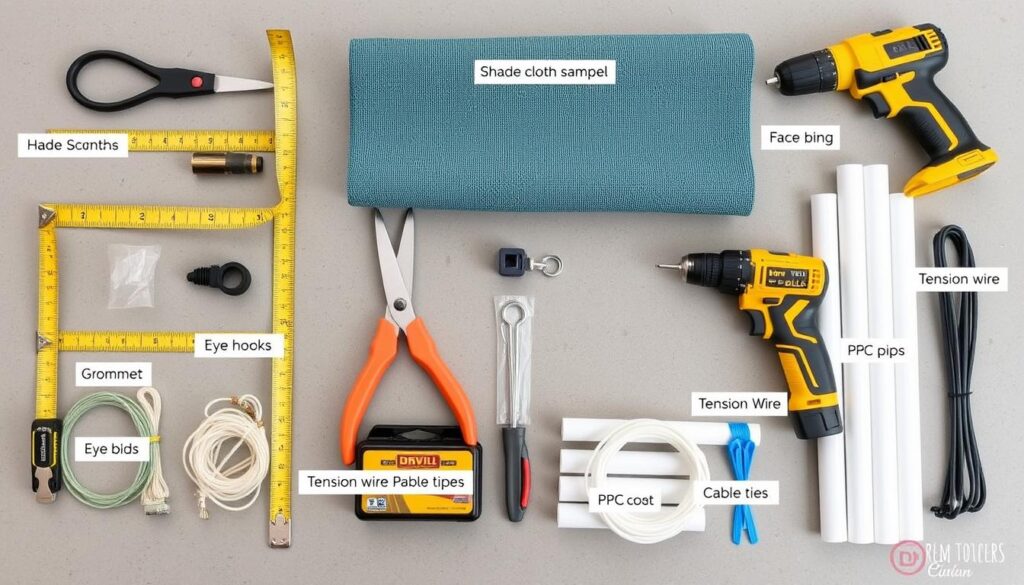

All tools and materials needed for your DIY vertical garden shade cover project
Installation Process: Mounting, Tensioning, and Adjustability
Measure your vertical garden structure and add 12 inches on all sides to allow for securing. Cut the shade cloth to size using sharp scissors or a utility knife.
Attach eye hooks or brackets to the wall, fence, or structure above and beside your vertical garden. Ensure they’re securely fastened and can support the tension of the shade cloth.

Properly installed eye hooks provide secure mounting points for your shade cover
For larger vertical gardens, create a lightweight frame using PVC pipes or aluminum poles to maintain proper distance between the shade cloth and plants (ideally 12-18 inches).
Install grommets around the perimeter of your shade cloth every 12-18 inches, or reinforce the edges with folded-over duct tape where you’ll attach zip ties.
Attach the shade cloth to your mounting points using carabiners, S-hooks, or UV-resistant zip ties. Start from the top and work your way down, ensuring even tension.

Secure the shade cloth with even tension using carabiners or UV-resistant zip ties
For larger installations, add horizontal and/or vertical tension lines using garden wire or thin rope to prevent sagging and wind damage.
Implement a simple pulley system or use bungee cords to make your shade cover adjustable, allowing you to retract it on cooler days or during morning hours.

Completed vertical garden shade cover installation with proper spacing and tension
Important: Maintain at least 12-18 inches of space between your shade cloth and plants to allow for proper air circulation. This prevents heat buildup and reduces humidity-related disease issues.
Design Options for Different Vertical Garden Setups
Your vertical garden’s specific configuration will determine the most effective shade cover design. Here are solutions for common vertical garden types:
Wall-Mounted Systems
Use an angled design that extends outward from the top, creating a tent-like cover. This allows hot air to escape upward while providing maximum shade.
Freestanding Vertical Gardens

Create a canopy-style cover that protects from above and on the south/west sides while leaving the north/east sides more open for airflow.
Balcony Vertical Gardens
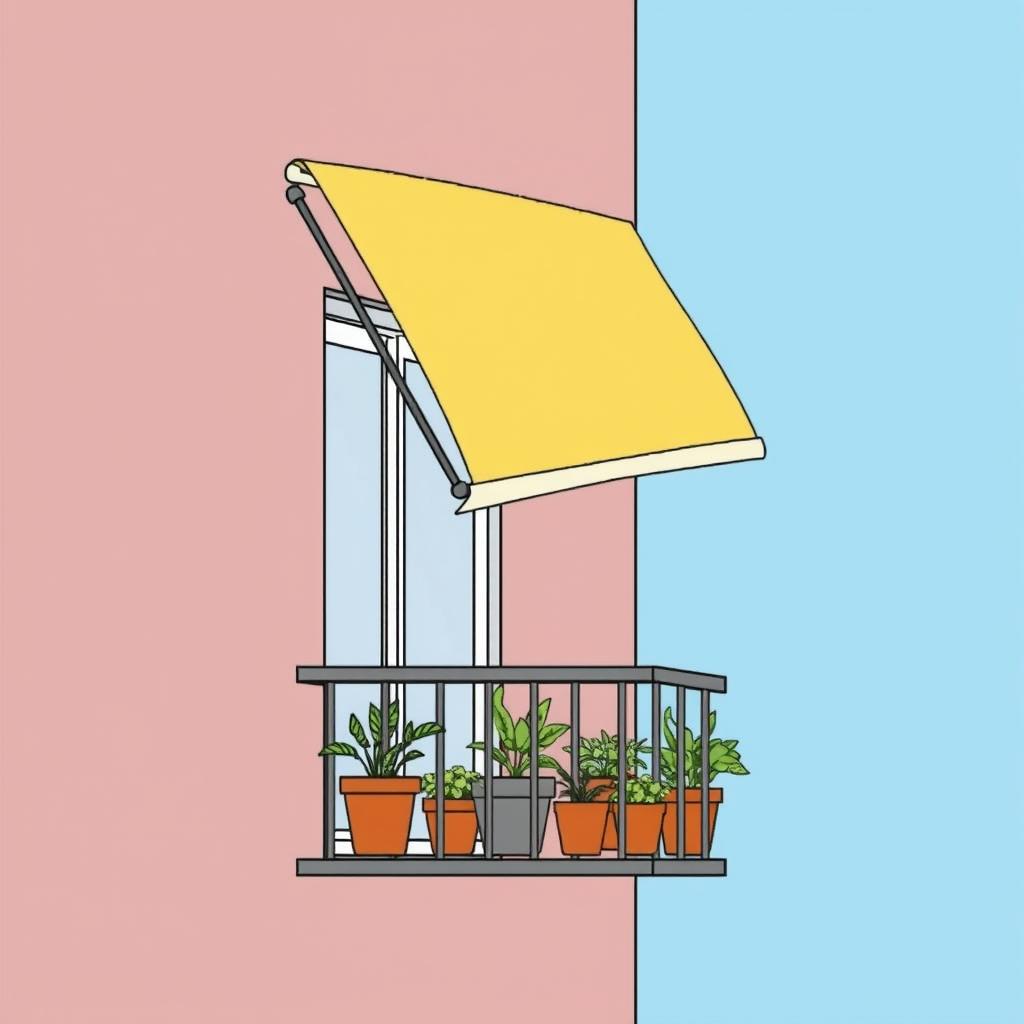

Implement a retractable roller shade that mounts to the balcony ceiling or railing, allowing easy adjustment throughout the day.
Customizing for Your Climate Zone
| Climate Zone | Recommended Shade % | Special Considerations |
| Desert (USDA 9b-11) | 50-70% | Use white or reflective materials; consider double-layer systems for extreme heat |
| Mediterranean (USDA 8-10) | 30-50% | Focus on afternoon shade; morning sun is beneficial |
| Tropical (USDA 10-13) | 30-40% | Prioritize airflow; use wider spacing between cloth and plants |
| Hot Continental (USDA 6-8) | 20-40% | Use adjustable systems to maximize sun during cooler periods |
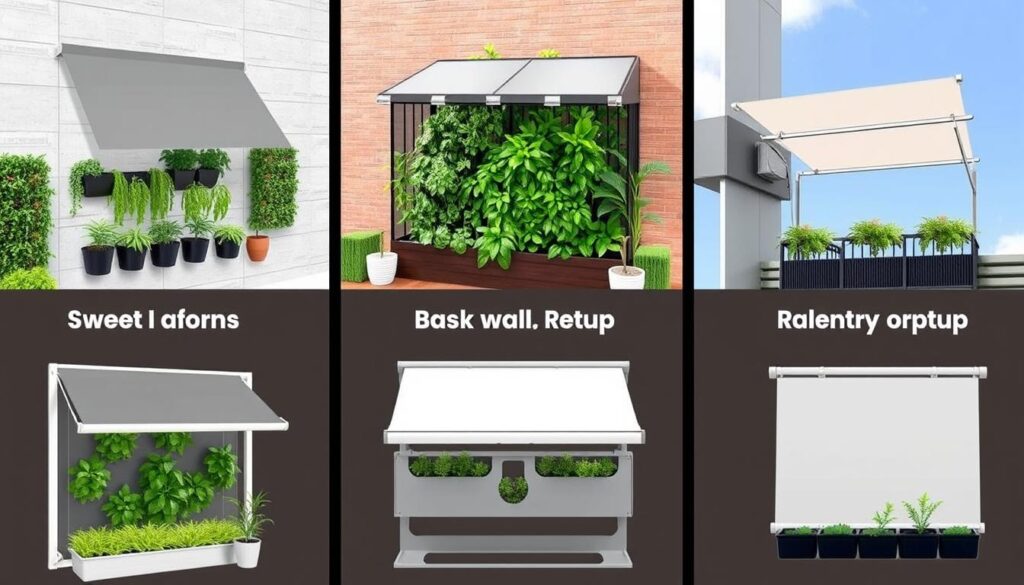

Shade cover designs optimized for different vertical garden configurations
Maintenance and Adaptations for Seasonal Changes
A well-maintained shade cover will last longer and perform better. Follow these maintenance tips and seasonal adjustments to get the most from your vertical garden shade system:
Routine Maintenance
- Regular Cleaning: Rinse dust and debris from your shade cloth monthly using a gentle spray of water.
- Check Tension: Inspect and adjust tension points after storms or high winds.
- Repair Small Tears: Address small tears immediately using UV-resistant thread or repair tape designed for shade cloth.
- Inspect Mounting Points: Check all hardware and mounting points twice per season for signs of wear or loosening.
Seasonal Adjustments
- Spring: Install partial shade as temperatures begin to rise above 85°F.
- Summer: Use maximum recommended shade percentage during peak heat.
- Fall: Gradually reduce shading as temperatures moderate.
- Winter: In mild climates, remove shade cloth entirely to maximize light. In frost-prone areas, consider using it for frost protection on sensitive plants.
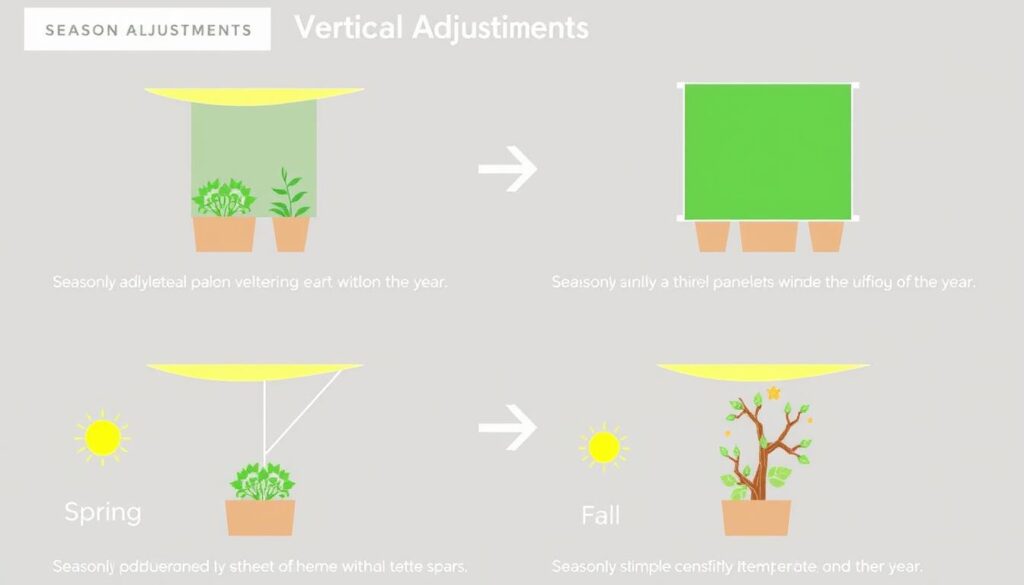
Adjust your shade cover configuration throughout the seasons for optimal plant growth
Weather Alert: Always remove or secure your shade cloth before severe storms or high winds. Even properly installed shade covers can become damaged or turn into sails during extreme weather events.
Storage Tips for Off-Season
When not in use, proper storage will extend the life of your shade cloth:
- Clean and thoroughly dry the shade cloth before storage
- Fold rather than crumple to prevent permanent creases
- Store in a dry, cool location away from direct sunlight
- Place in a breathable container or bag to prevent mildew
- Label with size and orientation to simplify reinstallation
Real-World Examples and Troubleshooting
My plants still look stressed despite having shade cloth. What’s wrong?
This usually indicates one of three issues:
- Insufficient shade percentage: You may need a denser shade cloth for your climate.
- Improper spacing: If the shade cloth is too close to plants, heat can get trapped. Ensure 12-18 inches of clearance.
- Inadequate watering: Even with shade, vertical gardens in high-heat zones need consistent moisture. Consider adding a drip irrigation system.
My shade cloth sags in the middle. How can I fix this?
Sagging is common with larger installations. Add support by:
- Installing a central support pole or crossbar
- Adding more tension points around the perimeter
- Creating an X-pattern of support wires under the cloth
- Using a more rigid shade material or combining with a lightweight frame
How do I prevent wind damage to my vertical garden shade cover?
Wind can quickly damage improperly secured shade covers:
- Use breakaway connectors that release under extreme tension
- Install the cloth with some slack rather than drum-tight
- Consider a retractable system you can quickly take down
- Use knitted rather than woven shade cloth (allows some air to pass through)
- Add wind slits in strategic locations if using a solid material
Can I use natural vines as a living shade cover for my vertical garden?
Yes! Living shade covers can be effective and beautiful:
- Fast-growing annual vines like hyacinth bean, moonflower, or morning glory work well
- Plant them on the south or west side of your vertical garden
- Provide a separate trellis for the vines to climb, positioned to cast shade on your vertical garden
- Be aware that living shade takes time to establish—use temporary cloth until vines fill in
This approach provides natural cooling through transpiration but requires additional watering for the shade plants.
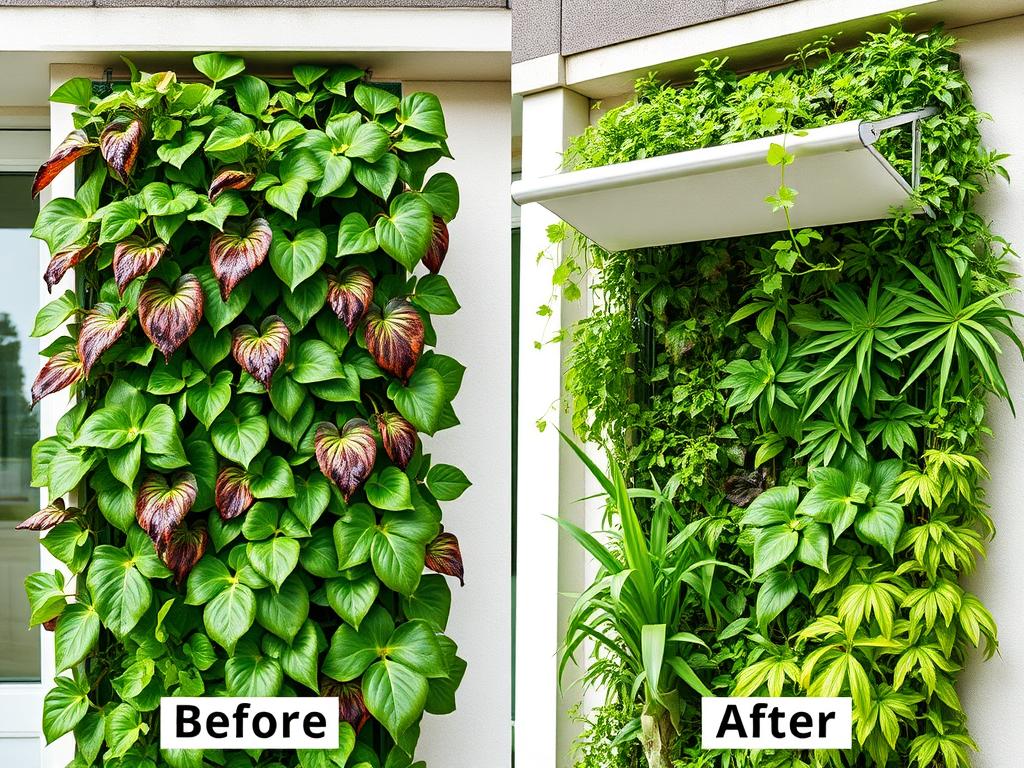

Before (left) and after (right): The dramatic difference a proper shade cover makes in high-heat conditions
I tried three different shade solutions for my balcony vertical herb garden in Phoenix before finding the perfect setup. The key was creating distance between the shade cloth and plants while still allowing morning sun exposure. My basil and cilantro now thrive through July when they used to burn up by May.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Vertical Garden Investment
A well-designed shade cover is not an optional accessory for vertical gardens in high-heat zones—it’s essential infrastructure that protects your investment of time, money, and effort. By following the guidelines in this article, you can create a customized shade solution that extends your growing season, reduces water consumption, and keeps your plants thriving even during the most challenging heat waves.
Remember that the perfect shade system often evolves through experimentation. Start with these fundamentals, observe your plants’ response, and make adjustments as needed. Your vertical garden’s microclimate is unique, and finding the ideal balance of sun and shade may take some fine-tuning.
With your new shade cover in place, you’ll be amazed at how much more productive and resilient your vertical garden becomes—turning what was once a challenging growing environment into a thriving oasis of greenery, even in the hottest months of the year.
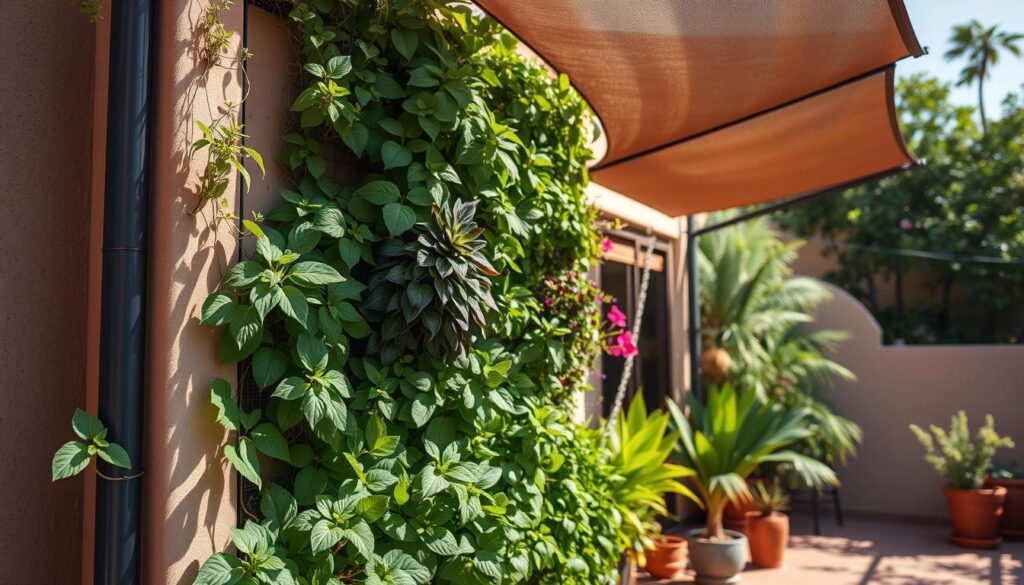

A properly shaded vertical garden can thrive even in the most challenging high-heat environments
Will is a vertical gardening enthusiast and sustainable cultivation specialist with a passion for helping people grow fresh food in small spaces and dry climates. With years of hands-on experience testing smart irrigation systems, optimizing urban gardens, and exploring eco-friendly solutions, this author shares clear, practical tips to turn any corner into a productive garden. Whether on a sunny balcony or in a compact backyard, Will helps readers save water, maximize space, and enjoy healthy harvests year-round. When not tending to his plants, you’ll find him sipping herbal tea and sketching ideas for new sustainable projects.

